As digital infrastructure pushes into the world’s most remote regions, Satellite IoT (Internet of Things) is emerging as a crucial enabler of ultra-wide coverage and always-on connectivity. From mountains and forests to oceans and deserts, satellite-powered communication is redefining what it means to be connected—especially in regions where terrestrial networks fall short.
In a major policy milestone, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) recently issued its Guidelines on Optimizing Market Access to Promote Satellite Communications Development. The document emphasizes encouraging the integration of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites with IoT applications, simplifying licensing, expanding spectrum coordination, and incentivizing real-world deployment.
Although China currently trails leaders like SpaceX’s Starlink in total satellite count, coverage, and commercial maturity, it is closing the gap through aggressive policy support, robust supply chain integration, and a maturing base of terminal technologies. As a result, China is quickly transitioning from a follower to a formidable player in the satellite IoT landscape.
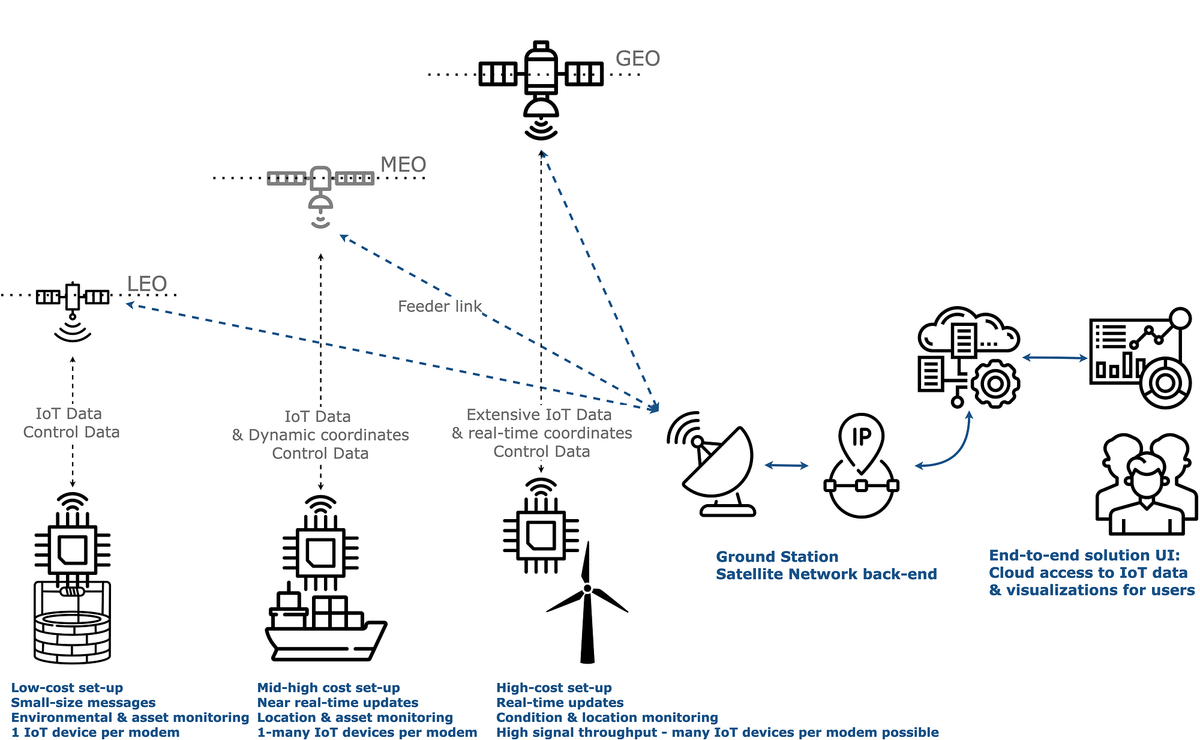
Types of IoT satellite networks,Source: Olga Kostina
A Global Trend: Satellite IoT’s Golden Decade Has Arrived
According to data from GSMA and NSR, by 2030, over 300 million satellite-connected IoT devices will be deployed globally across sectors like agriculture, logistics, energy, maritime, and environmental monitoring.
The three dominant product trends in this transformation include:
- NB-IoT NTN Modules Low-cost, low-power terminal modules that directly connect to satellites for efficient remote data transmission.
- Direct-to-Device (D2D) Smart Devices Smartphones, wearables, and industrial handhelds that support direct satellite messaging without extra hardware.
- Hybrid Edge GatewaysCombining LoRa, Wi-Fi, and satellite backhaul, enabling local networking in off-grid or harsh environments.
As industry standards such as 3GPP Release 17/18 for NTN (Non-Terrestrial Networks) evolve, interoperability between terrestrial and satellite networks will become the new norm. Chinese vendors are already developing NTN-compatible terminals and modules to meet this future head-on.
China’s Catch-Up Momentum: Gaps Remain, but Leverage Is Building
While Starlink has deployed over 6,000 satellites globally and already launched Direct-to-Cell services in regions like New Zealand and the U.S., China’s constellation coverage is still developing.
However, China’s unique strengths are becoming increasingly relevant:
- Alignment with global NTN standards, accelerating device and chipset readiness
- Vertically integrated IoT manufacturing chains, enabling fast iteration and cost control
- Fast-moving national policy, fostering a fertile environment for industry-wide collaboration
Leading Chinese firms such as Quectel, Fibocom, Jiutian Weixing, and others are actively exporting satellite-enabled terminals and systems into emerging markets across Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Why It Matters for Businesses: A New Era of Global-Scale Operations
Satellite IoT is not just a connectivity solution—it's a platform for entirely new business models and services:
- Logistics companies can now track containers and assets beyond cellular range.
- Farmers and agritech firms can monitor crops, soil, and livestock across remote farmland.
- Energy and utilities can oversee pipelines, solar farms, and wind turbines in uninhabited terrain.
- Emergency services can maintain communication and surveillance in disaster zones.
The result? Smarter, more efficient, and more resilient global operations—no matter where your business goes.
Localization Is Key: Winning in Global Markets Requires Localized Solutions
For enterprises looking to deploy Satellite IoT, success hinges not just on technology—but on regional adaptation and go-to-market execution:
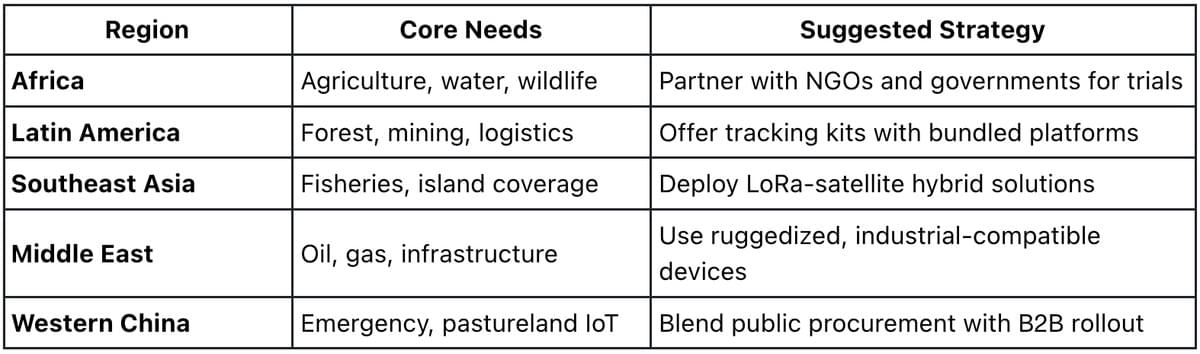
Those who combine satellite capability with local expertise will lead the next generation of IoT deployments.
Conclusion: From Earth to Orbit, the Real Race Has Just Begun
China is pushing hard to catch up in the satellite IoT sector. While it may not yet rival the scale of Starlink, its policy leverage, manufacturing strength, and ecosystem ambition position it well for long-term impact.
For global companies, this is not just a shift in infrastructure—it’s a once-in-a-decade opportunity to build new platforms, reach new markets, and redefine industry boundaries.
The next billion connected devices may not rely on towers—they may look to the sky.
Whoever moves fastest to adapt, localize, and scale will lead the future of global IoT—from the ground, all the way into orbit.
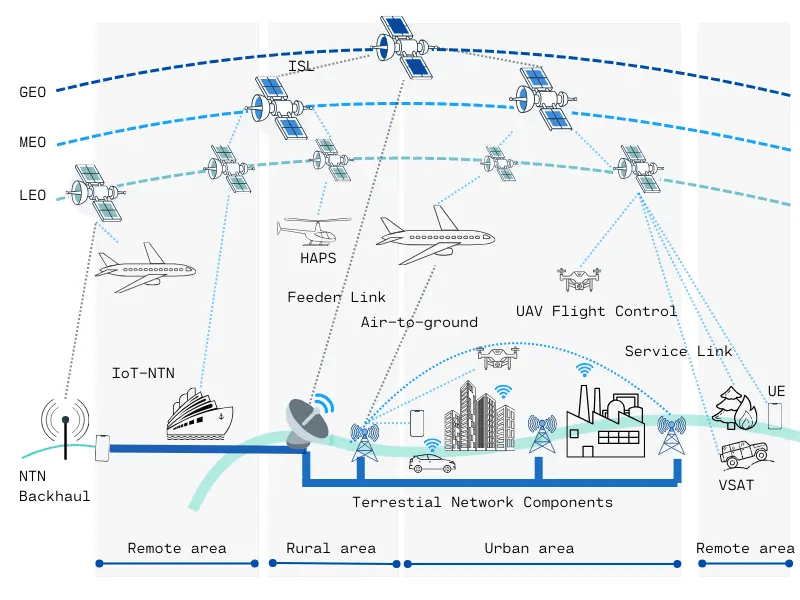
Types of IoT satellite networks,source:U-blox
Company Spotlight: Orbitmate Invites Global Partners to Build the Future of Satellite IoT
As an active player in the global satellite IoT ecosystem, Orbitmate is bridging the gap between space-based connectivity and terrestrial applications.We specialize in satellite IoT system solutions, integrating satellite resources from the United States, China, and other countries with the agility of China's mature IoT supply chain.
Our mission is to empower enterprises worldwide with scalable, globally-adaptable satellite IoT solutions.
We welcome device makers, solution providers, telcos, and regional partners to collaborate with Orbitmate in shaping the next generation of connectivity—across industries and across borders.
Let’s connect the unconnected—together.
📞 WhatsApp: +1 878 166 5352
📧 Email: info@orbitmate.com
End