1. Overview of the Acquisition Case
On September 8, 2025, SpaceX announced the acquisition of EchoStar's AWS-4 and H-block spectrum licenses for $17 billion. The deal includes $8.5 billion in cash, $8.5 billion in SpaceX stock, and assuming EchoStar's debt interest of approximately $2 billion. The deal structure is as follows:
Through this acquisition, SpaceX has obtained approximately 50 MHz of S-band spectrum resources, including the AWS-4 (2000-2020 MHz and 2180-2200 MHz) and H-block (1915-1920 MHz and 1995-2000 MHz) frequency bands. These spectra are regarded as the "golden frequency bands" for satellite direct-to-mobile services, with good signal propagation characteristics and compatibility with both terrestrial and satellite networks.
Notably, the FCC launched a spectrum usage compliance investigation (Case No. SB Docket No. 25-173) against EchoStar on May 12, 2025, alleging underutilization of its 2GHz and AWS-4 frequency bands. After the completion of this transaction, the FCC terminated the investigation on September 10, clearing regulatory hurdles for SpaceX.
2. EchoStar Business Operations and Core Values
EchoStar, an established US satellite communications company founded in 1980, owns Dish Network satellite TV service and Boost Mobile Mobile Market under its umbrella. The company's main business is divided into three major segments: pay TV, wireless network services, and satellite broadband and enterprise business.

EchoStar Company Headquarters
By the end of 2024, EchoStar's pay-TV business revenue was $10.673 billion (accounting for 67.44%), wireless revenue was $3.605 billion (accounting for 22.78%), and broadband and satellite service revenue was $1.547 billion (accounting for 9.77%). However, this established satellite company has been deeply mired in financial difficulties in recent years. As of before the transaction, EchoStar's total liabilities reached as high as $26.4 billion, and it had a net loss of $306 million in the second quarter of 2025.
Spectrum assets are the core value of EchoStar . The company sold the 600MHz and 3.45GHz spectrum bands to AT&T for $23 billion and the AWS-4 and H-block spectrum to SpaceX for $17 billion, with a total transaction size of $40 billion setting an industry record. The consideration for the spectrum asset transaction is 27 times higher than EchoStar's acquisition of Boost Mobile in 2019 ($1.4 billion), highlighting the scarcity of high-quality spectrum resources in the era of satellite-mobile convergence.
3. Acquisition Motivation and Strategic Value of SpaceX
1. Spectrum Resources
For SpaceX, this acquisition has addressed a key bottleneck in the development of its Starlink business. By June 2025, Starlink had achieved coverage of over 5 million users, serving more than 100 countries worldwide, but there were significant shortcomings in direct-to-mobile services.
Previously, Starlink'sdirect-to-cell service needed to cooperate with terrestrial operators such as T-Mobile, borrowing the latter's cellular spectrum as a "secondary service" to fill coverage blind spots. This approach is complex, costly, and limited in terms of frequency selection, on-ground usage, and user relationship development.
After acquiring EchoStar's spectrum, SpaceX will obtain independent spectrum resources, enabling it to independently deploy a global network and reduce its reliance on terrestrial operators. SpaceX plans to utilize these spectra to increase its cellular communication capacity by more than 100 times, with the goal of achieving large-scale commercialization by 2026.
The specific distribution of spectrum resources acquired through acquisition is as follows:
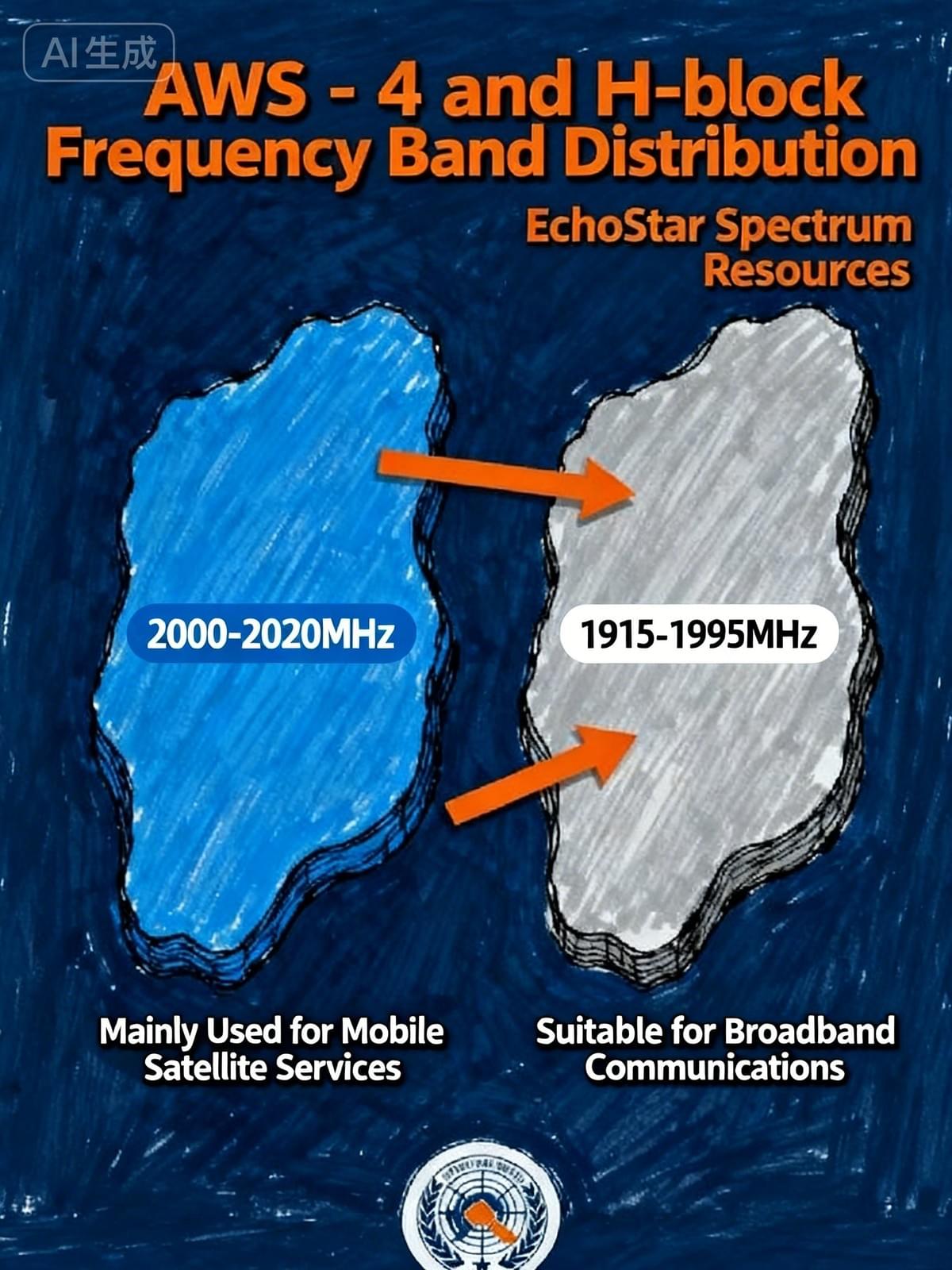
AWS-4 band: 2000-2020 MHz and 2180-2200 MHz, mainly used for mobile satellite services
H-block frequency band: 1915-1920MHz and 1995-2000MHz, suitable for broadband communication services
2. Customer and Collaboration
EchoStar brings more than just spectrum resources to SpaceX. As part of the deal, approximately 7 million users of Boost Mobile, a mobile virtual network operator under EchoStar, will be able to access SpaceX's Starlink Direct-to-Cell service. This means that these users can stay connected via Starlink satellites in remote areas not covered by traditional terrestrial networks without having to replace their phones or SIM cards, which provides SpaceX with an established user base and market channels.
Beyond its well-defined spectrum and customers, EchoStar, as an established satellite communications enterprise, haspatents and experience accumulated in satellite broadband products, hardware equipment, spectrum management, and engineering services, which also exhibit high complementarity with SpaceX's Starlink program. These intangible "resources" are also expected to have a positive impact on SpaceX's future technology development and network operations.
4. Global Satellite Communication Market Landscape and Competitive Dynamics
(1). Market Size and Growth Forecast
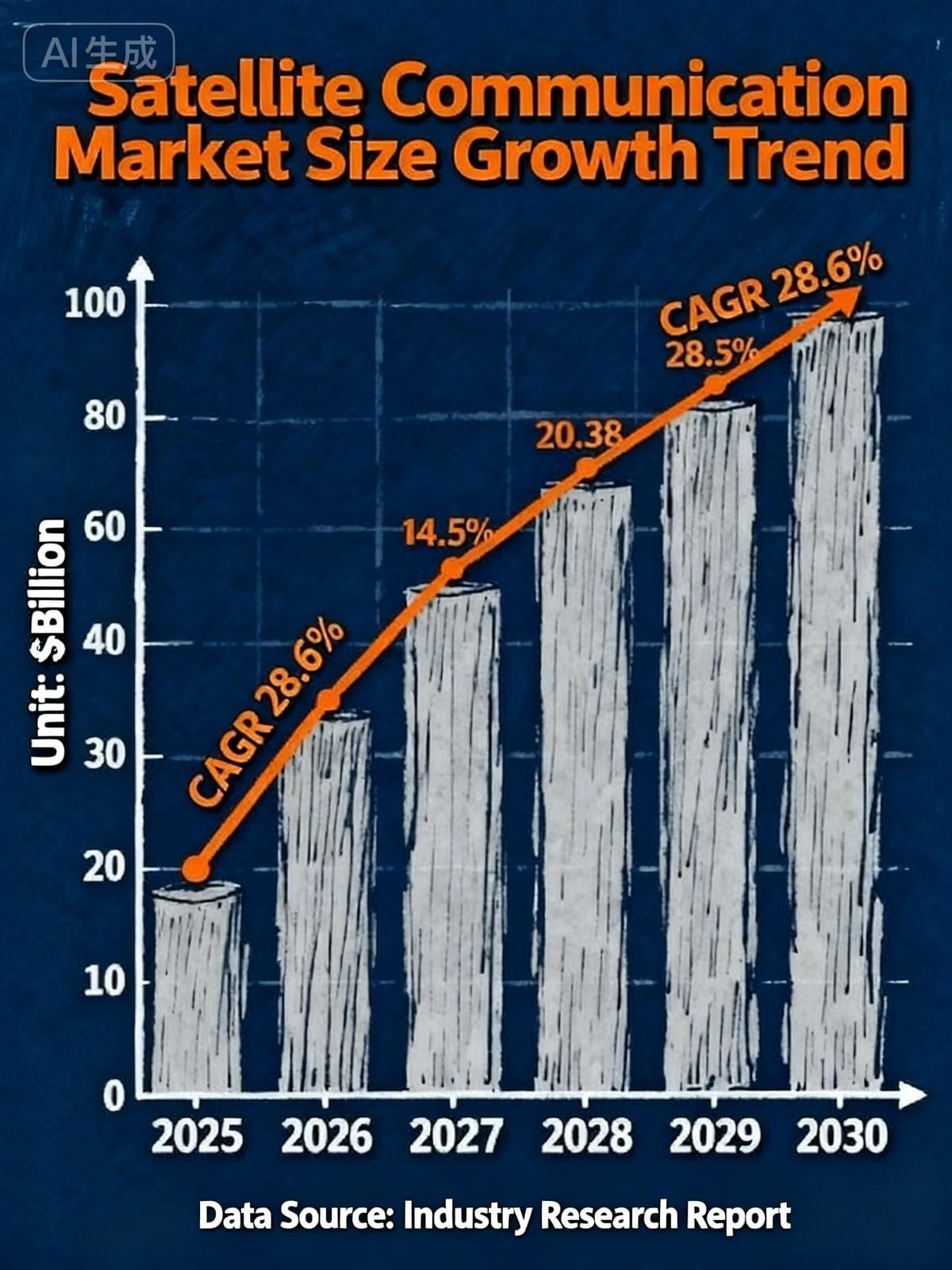
The global mobile satellite services market size has exceeded $12 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.6% from 2025 to 2030, and is expected to exceed $200 billion by 2030.
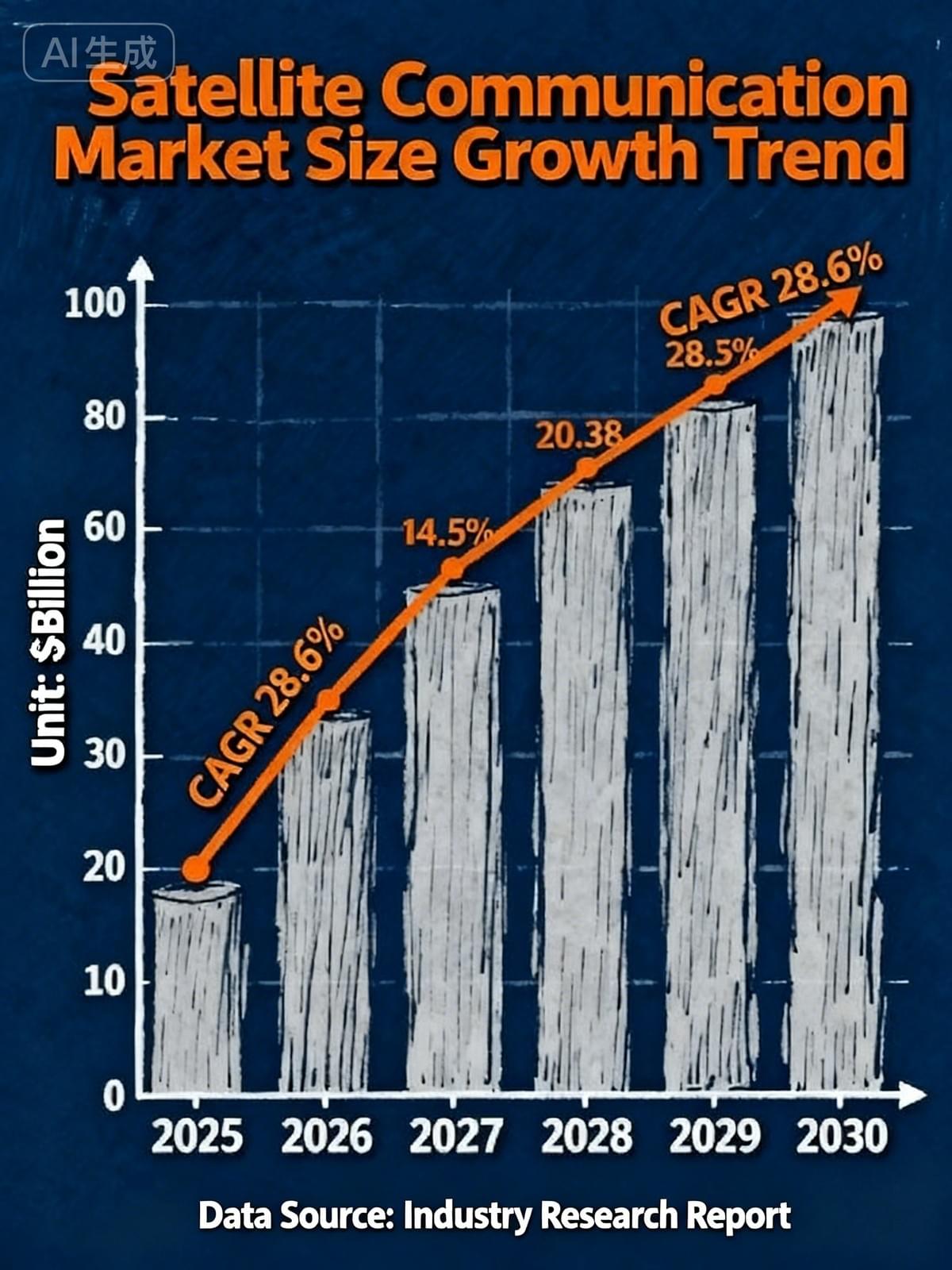
From a segmented perspective, satellite broadband services have seen particularly significant growth. EchoStar's broadband and satellite services segment recorded revenues of $340 million in the second quarter of 2025, with the company's order backlog increasing by 8% to $1.6 billion, reflecting the growing demand for high-reliability satellite communications in the enterprise market.
(2). Comparison of Strategic Layouts of Major Competitors
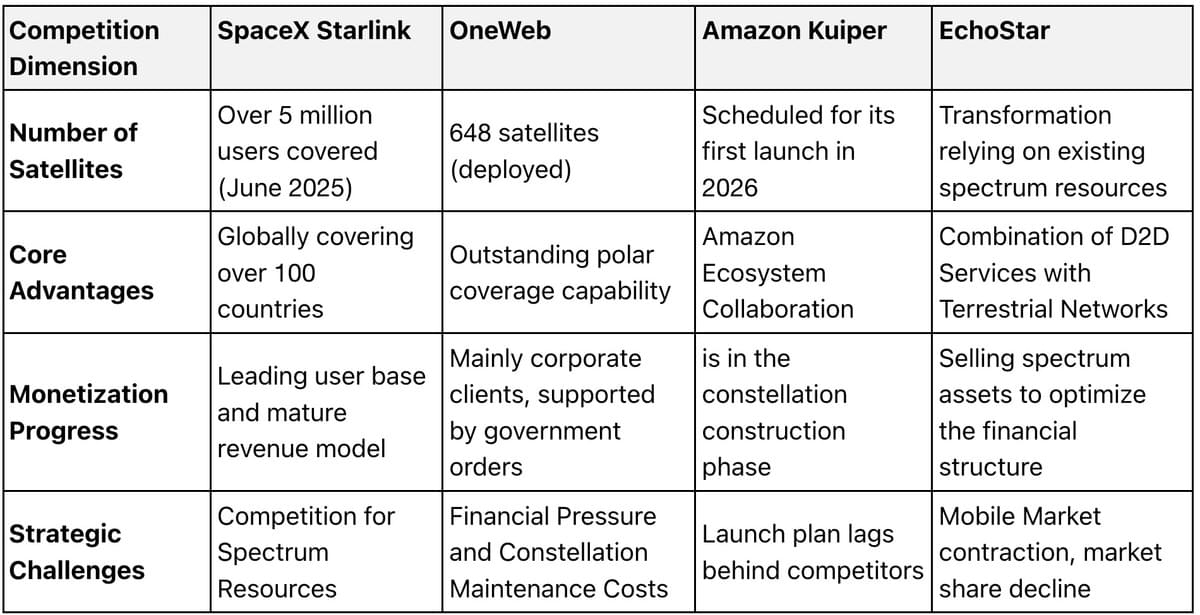
The current global satellite communication market presents a multi-power competition landscape , with companies such as SpaceX, OneWeb, Amazon Kuiper, and EchoStar seizing market share through differentiated paths:
5. Layout and Progress of China's Satellite Communication Business
(1). Policy Framework and Development Goals
In August 2025, the MIIT issued the "Guiding Opinions on Optimizing Business Access to Promote the Development of the Satellite Communications Industry" (MIIT Letter Management [2025] No. 180), proposing the goal of developing more than 10 million satellite communications users by 2030.
The guiding opinions propose 19 specific measures, including orderly expanding market opening, developing low-orbit satellite internet, achieving global broadband network coverage, supporting telecommunications operators in carrying out end point equipment direct connection to satellite services through co-construction and sharing, and organizing and conducting commercial trials of satellite Internet of Things.
(2). Progress of the Core Constellation Project Construction
China has established a constellation construction pattern of "dominated by national teams and supplemented by private enterprises". By August 2025, the total number of planned satellites has exceeded 32,000, including 3 constellations with a scale of 10,000 satellites, forming a coordinated development system of high, medium, and low orbits.
a. China StarNet GW Constellation (core project of the national team)
Constellation architecture: 12,992 satellites, deployed in two sub-constellations
GW-A59: 6,080 satellites, distributed in very low orbits below 500 km, providing low-latency broadband services
GW-A2: 6912 satellites, deployed in a 1145km orbit, to achieve global seamless coverage
Construction Progress:
December 2024: The first launch of "10 satellites on a single rocket" kicks off the network construction.
July - August 2025: Set a record of intensive launches with "two launches in three days", with a cumulative total of 72 satellites successfully placed into orbit
2030 Goal: Complete the deployment of 1,300 satellites to meet the requirements of the ITU's "7-Year Rule"
b. Qianfan Constellation (monetization benchmark project)
Implementation entity: Shanghai Yuanxin Satellite Technology (with Shanghai state-owned assets background)
Scale planning: 15,000 low-orbit satellites, to be built in three phases
Phase 1 (2025): 600 satellites, covering the Asia-Pacific region
Phase II (2027): 1,296 satellites, achieving global service capabilities
Phase III (2030): Complete the constellation of 15,000 satellites and provide full coverage
c. Hongyan and Hongyun Projects (traditional central state-owned enterprise projects)
Hongyan Constellation (China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation):
300 low-orbit satellites, specializing in narrowband IoT communication
After the completion of Phase II in 2025, global IoT end point connectivity will be achieved
Application scenarios: smart meters, ocean monitoring, wildlife tracking
Hongyun Project (China Aerospace Science & Industry Corporation):
A broadband communication system consists of 156 satellites, with each satellite having a capacity of 20 Gbps
Progress is slow. Currently, only technology verification satellites have been launched, and mass deployment has not yet begun.
d. Supplementary layout of private constellations
GalaxySpace: 8 test satellites in orbit, plans to deploy 1,000 low-orbit satellites
Geely Future Mobility Constellation: 21 satellites in orbit, serving intelligent vehicle positioning and communication
Guodian Gaoke Tianqi Constellation: 34 satellites in orbit, focusing on low-power IoT communication
(3). Operator Progress
As a pioneer in the domestic satellite communication field, China Telecom has seen its direct-to-satellite mobile phone users exceed
nearly 3 million by September 2025. China Unicom obtained the satellite mobile communication business operation license issued by the MIIT on September 8, 2025, and China Mobile is applying for the relevant license.
(4). Outlook
By 2030, China will have established a relatively complete satellite communication system, forming a "1+N" constellation pattern (1 national backbone constellation + N professional application constellations), with the market size expected to exceed 200 billion yuan and occupy 20% of the global low-orbit satellite market. The Application Area will achieve a transformation from "supplementary to integrated", becoming a core component of the 6G network and providing full-domain connectivity capabilities for emerging scenarios such as intelligent driving and telemedicine.
6. Insights and Outlook
SpaceX acquires EchoStar for $17 billion, obtaining AWS-4 and H-block prime spectrum,
breaking through the bottleneck of direct mobile connectivity, achieving spectrum autonomy and global network deployment, and integrating Boost Mobile's 7 million users to strengthen synergy. This transaction marks a new stage of "spectrum competition" in satellite communications and propels the industry towards "full-domain integration." In global competition, China will basically achieve its phased goals by 2030 through the constellation layout of "national team + monetization." In the future, it will become the core G, empowering scenarios such as intelligent driving and telemedicine, and reshaping the global communication infrastructure landscape.
End